Pneumatic Compression Device For Dvt Prophylaxis

One hundred fifty three patients had neither pe nor dvt clinically or by doppler studies one patient had a venographically proven dvt and one patient had a clinical.
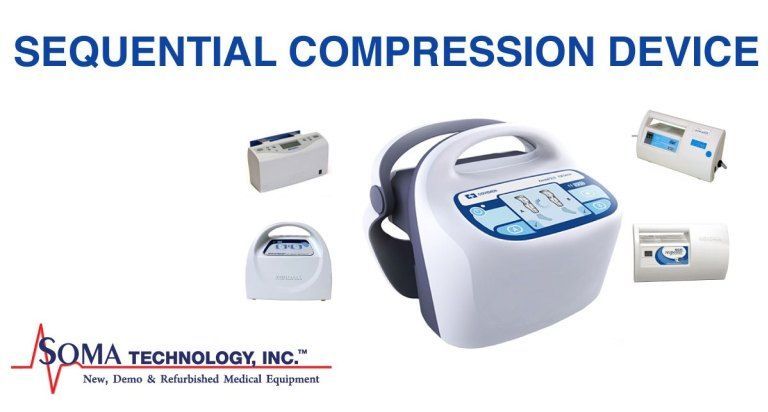
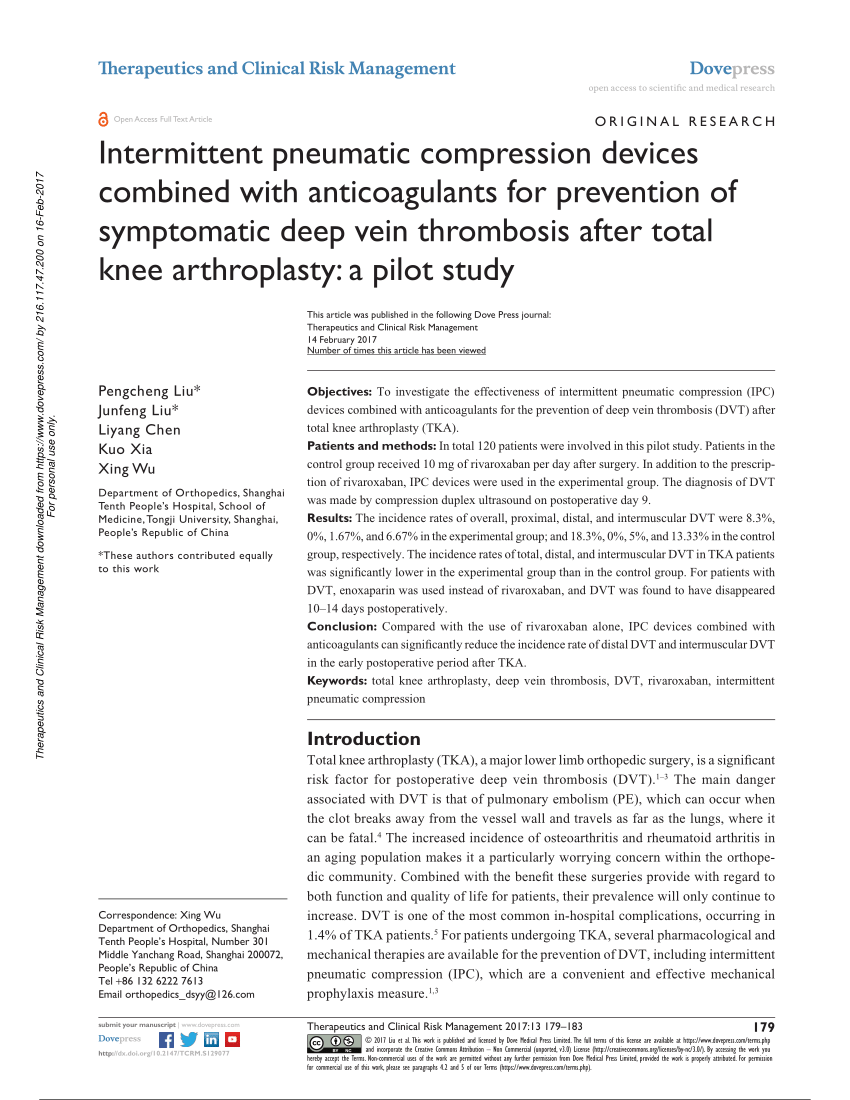
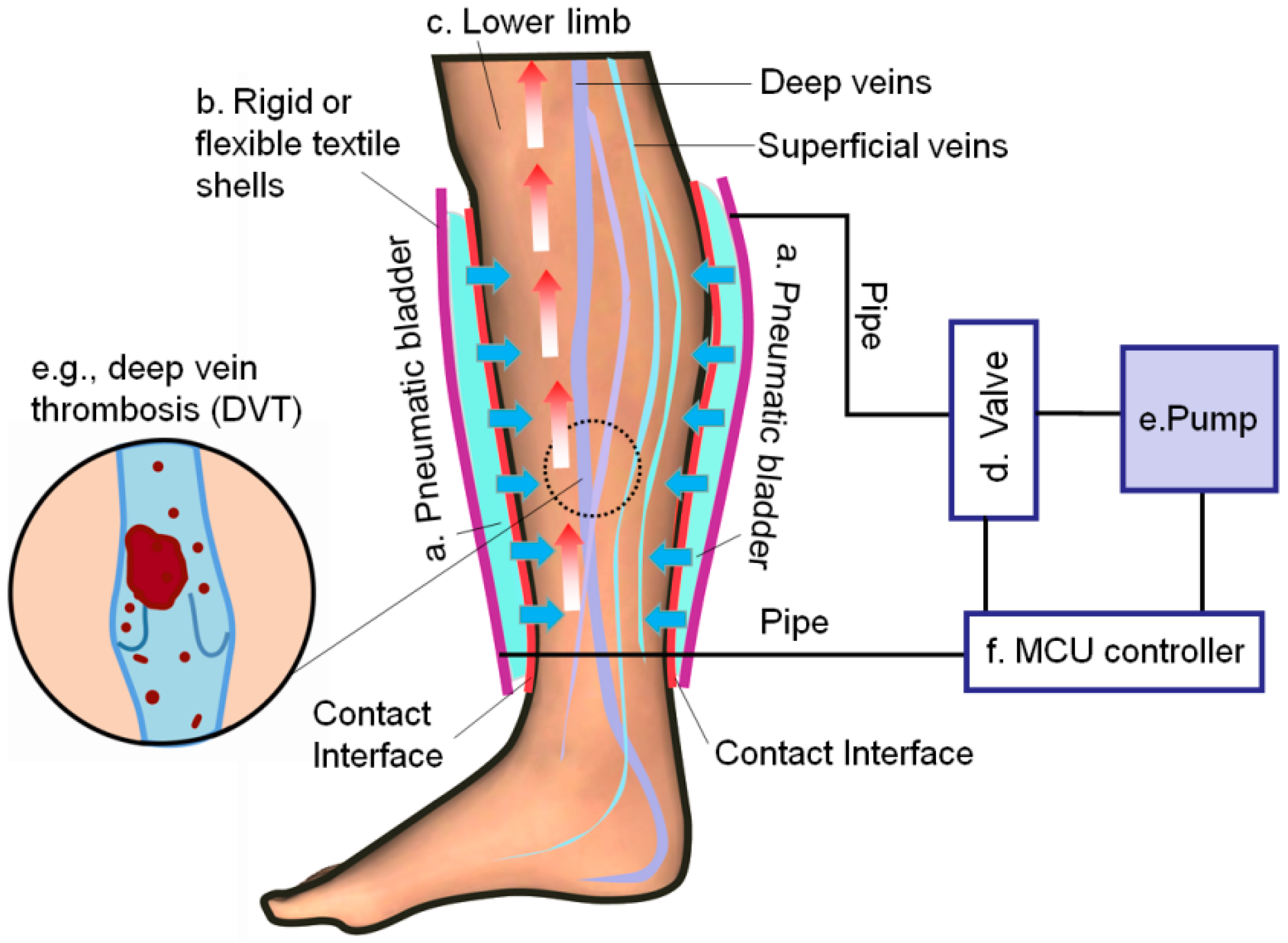
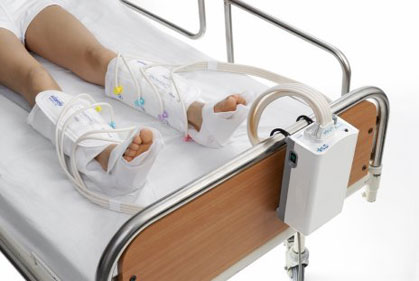
Pneumatic compression device for dvt prophylaxis. There are different opinions about whether or not prophylaxis should be used in knee arthroscopy partly reflecting different perceptions of the underlying risk of dvt. A study comparing a rapid inflation asymmetrical compression device by venaflow with a sequential circumferential compression device by kendall in a high risk post knee replacement population produced dvt rates of 6 9 versus 15 respectively p 007. Another meta analysis ho and tan 2014 reviewed 70 trials with a total of 16 164 patients 3 this analysis concluded that intermittent pneumatic compression devices were effective in reducing the incidence of dvt and combining this with pharmacological prophylaxis was more effective than mechanical devices alone. Compliance is often suboptimal 23 24.
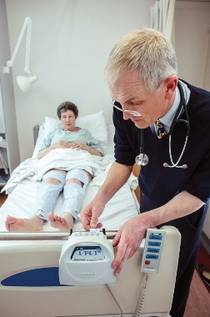
I would consider adding compression devices for particularly high risk patients but for most patients heparin or low molecular weight heparin alone should suffice. There is a large body of evidence documenting that intermittent pneumatic compression ipc is effective in preventing deep vein thrombosis dvt in hospitalized high risk patients. A pneumatic compression device was applied to 155 patients with a normal doppler venous examination who underwent a general surgical procedure of at least 1 hr in duration. 16 17 furthermore the type of sleeve and device may affect comfort and compliance as some.
Although pneumatic compression likely is useful if a patient has a contraindication to pharmacologic prophylaxis routine dual vte prophylaxis use warrants reconsideration. Although pneumatic compression likely is useful if a patient has a contraindication to pharmacologic prophylaxis routine dual vte prophylaxis use warrants reconsideration. Although ipcds can offer protection against vte 20 22. 1 8 early randomized studies show a significant reduction in venographically proven dvt following total hip and knee replacement.
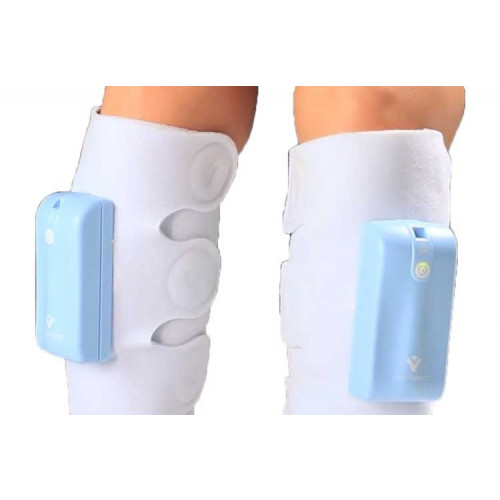
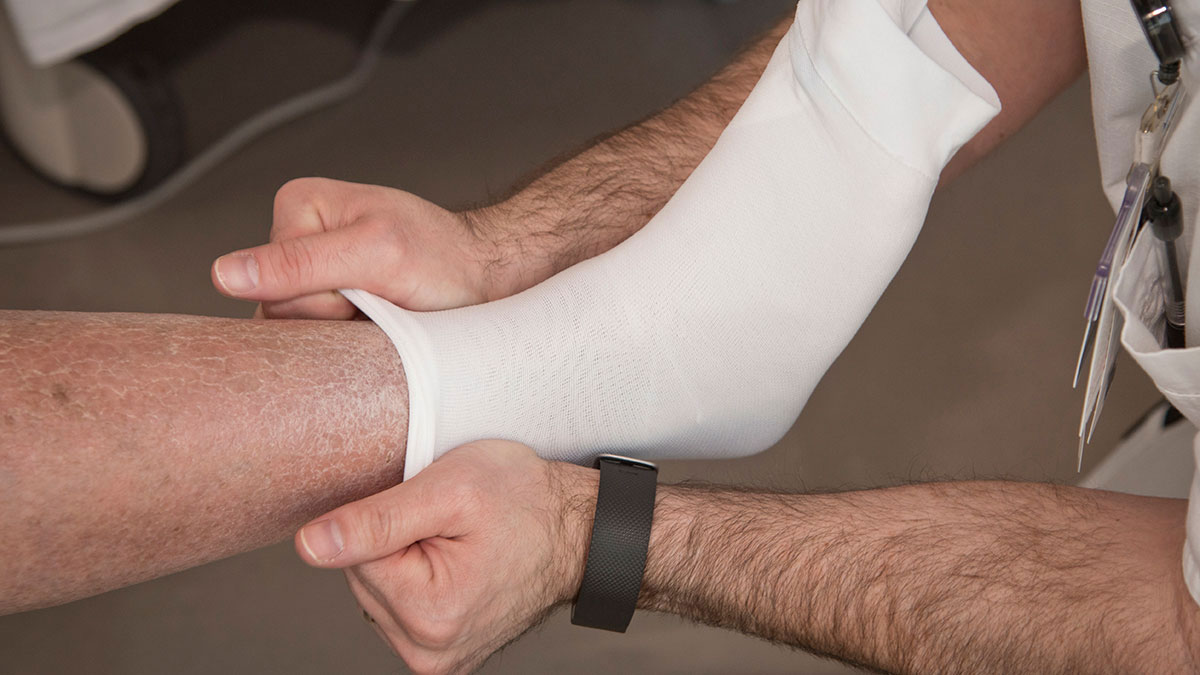
Combined intermittent pneumatic leg compression and medication for the prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism background deep vein thrombosis dvt and pulmonary embolism pe are collectively known as venous thromboembolism vte and occur when a blood clot develops inside the leg veins dvt and travels to the lungs pe. Intermittent pneumatic compression ipc devices are used to help prevent blood clots in the deep veins of the legs. Mechanical prophylaxis with intermittent pneumatic compression devices ipcds is recommended particularly in populations at high risk of bleeding 13 16. I would consider adding compression devices for particularly high risk patients but for most patients heparin or low molecular weight heparin alone should suffice.
Due to the decreased risk of major bleeding and surgical site bleeding associated with ipcds. This increases blood flow through the veins of your legs and helps prevent blood clots.