Plasma Nitriding Of Hp13cr Super Martensitic Stainless Steel

Table 1 compares the difference in their capacity inner nitriding behavior and characteristics together.
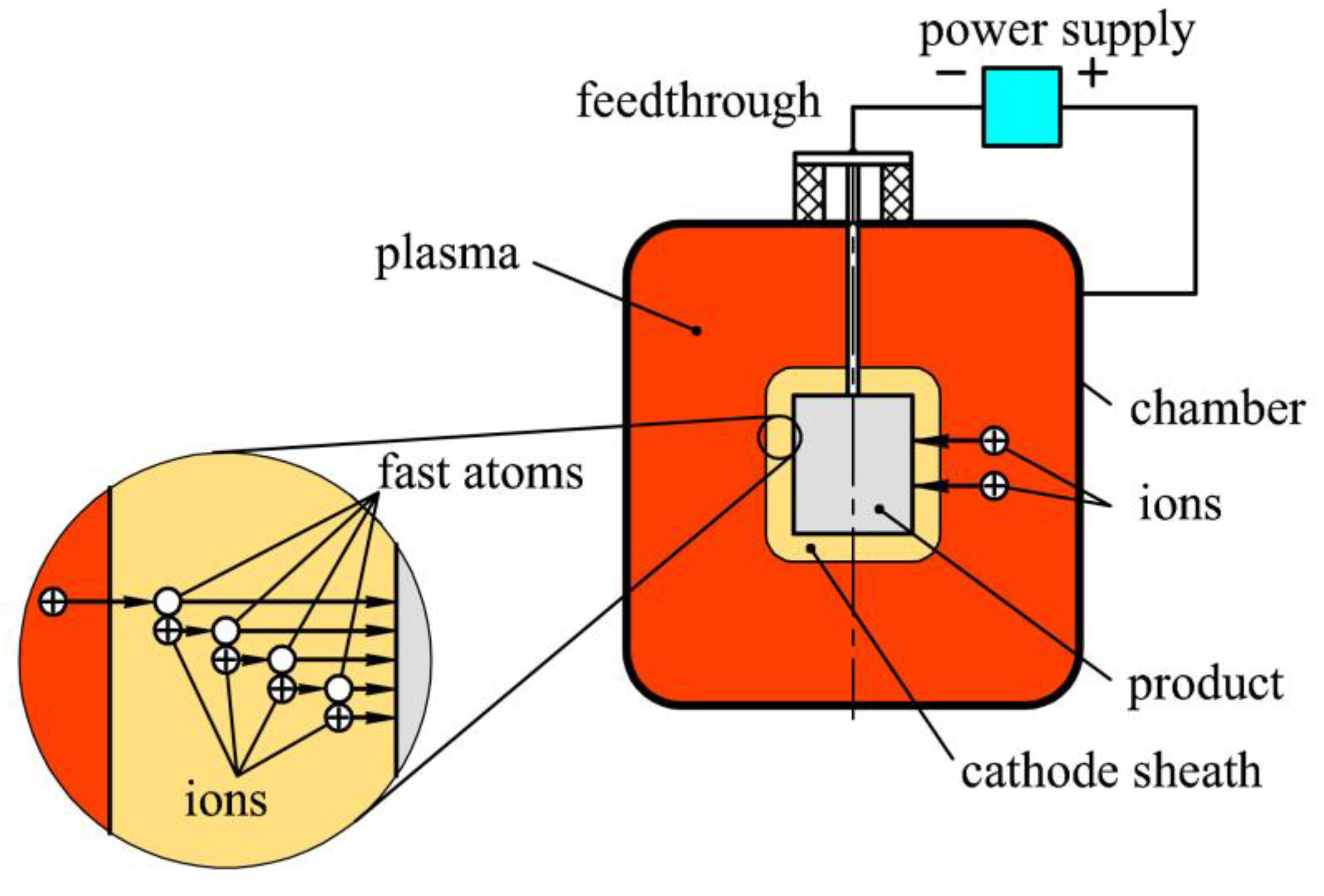
Plasma nitriding of hp13cr super martensitic stainless steel. Cr martensitic steels lower in carbon and with additional alloying of nickel and molybdenum offering better weldabilty and low temperature toughness. Solution nitriding of martensitic stainless steels is an efficient and economical surface hardening process when high pressure gas quenched in situ in a vacuum furnace. Nitriding time will depend on the case depth desired and can be calculated from fick s law 2. The system consisted of a 100 l stainless steel chamber connected to a high voltage power supply up to 25 kv and 1 a with frequency 0 5 4 khz and pulse width 10 50 μs control.
The results of nitriding experiments for some martensitic stainless steels show that plasma nitriding can produce a certain thickness of nitriding layer on the surface of stainless steel plates and there is no need to remove the oxide film pretreatment. The high diffusivity and low solubility of nitrogen in the martensitic structure allowed the production of thick layers 16 61 m containing fe 2 3n fe. Dc plasma and dc pulse plasma 18 19 20 have been utilized for nitriding of stainless steel parts tools and dies at higher hold temperature than 800 k. Several works have shown that plasma nitriding and nitrocarburizing of stainless steels at low temperatures produces a hard surface layer which results in increased wear resistance.
The surface properties of these steels. The alloys used for the plasma nitriding treatments are. The hardness and wear resistance of the stainless steel after nitriding will be obviously enhanced. In the present work hp13cr smss with a fully martensitic microstructure were plasma nitrided in the 350 450 c range.
Nitriding was performed in h2 n2 gas mixtures for 5 10 and 20 n2 in. Aisi 316l austenitic stainless steel aisi 409 ferritic stainless steel and astm super duplex a890 gr5a steel all in the solubilized conditions. Supermartensitic stainless steel hp13cr was plasma nitrided at temperatures 350 400 and 450 c. The starting condition was a fully martensitic microstructure achieved by heat treatment at 1100 c and oil quenching.
In addition lower friction coefficients could be reached indicating a better tribological performance of the nitrided steel in comparison to the base material. Plasma nitriding of 410s ferritic martensitic stainless steel proved to be efficient in increasing the abrasive wear resistance of the relatively soft base material. The nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation was carried out using piii 25 equipment from plasma liits brazil. Plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition pecvd has been utilized for nitriding at lower temperature than 800 k.